Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) organisations play an essential role in preparing individuals for the workforce by imparting practical skills and knowledge. Ensuring the continuous professional growth of TVET trainers is essential for several reasons, each with significant implications for learners, educational institutions, and the broader economy. This article explores why supporting teacher development in TVET is so important, integrating the five-stage theory of teacher development proposed by Dreyfus and Dreyfus (1986), and offers strategies for achieving this goal.
Dreyfus and Dreyfus Five-Stage Theory of Teacher Development
Dreyfus and Dreyfus (1986) proposed a five-stage model that outlines how individuals progress from novice to expert in any field, including teaching. Understanding this model can help TVET organisations tailor their support strategies effectively.
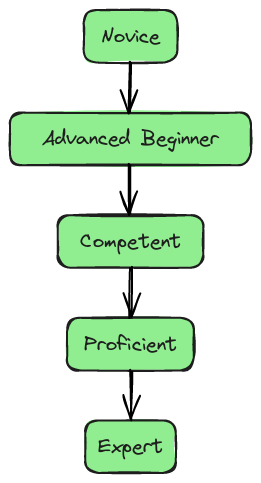
- Novice: New trainers who rely heavily on rules and guidelines.
- Advanced Beginner: Trainers who start recognising patterns and contexts but still need frequent feedback.
- Competent: Trainers who can plan and manage classes independently and make informed decisions based on past experiences.
- Proficient: Trainers with an intuitive grasp of complex situations who can adapt their teaching strategies flexibly.
- Expert: Trainers with a deep and comprehensive understanding of their field who operate effortlessly and innovatively.
Enhancing Teaching Quality
Continuous professional development ensures that TVET trainers progress from novice to expert, enhancing their teaching quality. Improved teaching techniques directly lead to better learner outcomes, making education more engaging and effective. Up-to-date knowledge ensures that the skills taught are relevant and applicable, facilitating a high-quality learning environment that benefits learners and educators.
Adapting to Industry Changes
The vocational and technical fields are dynamic, with frequent technological advancements, processes, and standards. TVET trainers need to stay current to provide relevant education. By incorporating the latest industry practices into their teaching, trainers prepare learners to enter the workforce with up-to-date skills. This alignment with industry needs enhances employability and ensures that the training programmes remain relevant and competitive.
Meeting Diverse Learner Needs
TVET programmes attract diverse learners with varying backgrounds, learning styles, and needs. Skilled trainers can adapt their teaching to cater to this diversity, increasing their ability to differentiate instruction and support individual learner needs. This adaptability leads to higher learner satisfaction and retention rates, as learners feel more supported and engaged in their educational journey.
Promoting Lifelong Learning
Cultivating a culture of continuous improvement and professional growth among trainers promotes the concept of lifelong learning. Trainers who model the importance of ongoing education and self-improvement encourage learners to pursue continuous personal and professional development. This learning culture extends beyond the classroom, contributing to the broader educational community and society.
Enhancing Institutional Reputation
Institutions that support their staff’s professional development tend to attract high-quality trainers and learners. An enhanced reputation can increase enrolment and funding opportunities, attracting skilled trainers committed to their own and their learners’ growth. This positions the institution as a vocational and technical education leader, benefiting both the organisation and its stakeholders.
Improving Workforce Readiness
Effective TVET training directly impacts workforce readiness by ensuring learners have the skills that employers need. Graduates more competent and confident in their abilities help reduce the skills gap in various industries. This, in turn, contributes to economic growth by providing a skilled and adaptable workforce ready to meet the demands of the modern economy.
Encouraging Innovation and Best Practices
Supporting trainer development encourages innovation in teaching methods and best practices. Trainers are likelier to experiment with and implement innovative strategies, promoting a culture of excellence and continuous improvement. This also facilitates the sharing of best practices within and between institutions, enhancing the overall quality of education.
Enhancing Trainer Wellbeing and Job Satisfaction
Ongoing professional development and support contribute significantly to the well-being and job satisfaction of TVET trainers. Providing growth and advancement opportunities reduces burnout and turnover, increases motivation, and promotes a more positive and supportive work environment. Satisfied and well-supported trainers are more effective in their roles, benefiting learners and the institution.
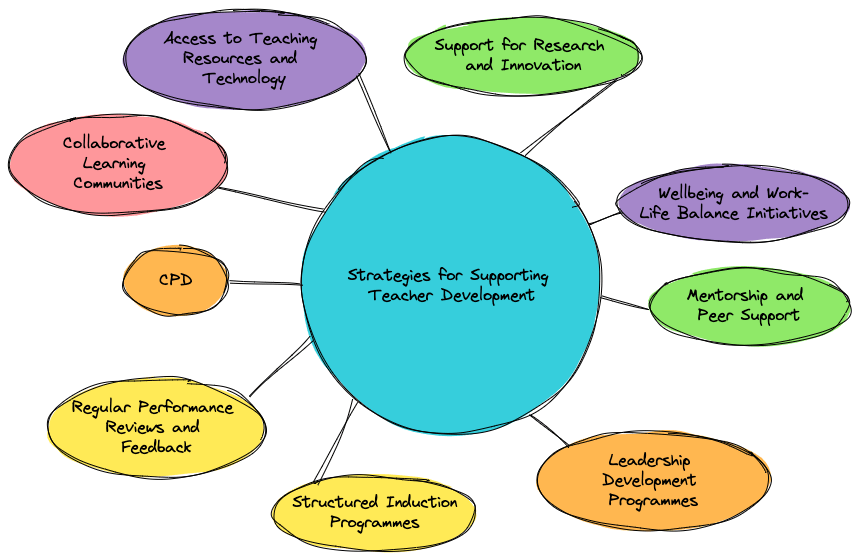
Strategies for Supporting Teacher Development
To achieve these benefits, TVET organisations can implement several support strategies aligned with the Dreyfus and Dreyfus model:
- Structured Induction Programmes: These programmes help new trainers (novices) transition smoothly into their roles by familiarising them with organisational policies, teaching resources, and support systems.
- Mentorship and Peer Support: Pair less experienced trainers (novices and advanced beginners) with seasoned professionals to provide guidance, feedback, and a platform for sharing best practices.
- Continuous Professional Development (CPD): Offer regular workshops, further education opportunities, and support for attending conferences and professional networking events to help trainers move from competent to proficient and expert stages.
- Access to Teaching Resources and Technology: Provide trainers with up-to-date textbooks, online resources, teaching aids, and training on digital tools and educational software.
- Collaborative Learning Communities: Create opportunities for trainers to collaborate and learn from each other through regular meetings, planning sessions, and sharing platforms.
- Regular Performance Reviews and Feedback: Conduct annual appraisals, peer reviews, and self-assessment opportunities to provide constructive feedback and aid in progression through the development stages.
- Support for Research and Innovation: Encourage trainers to engage in research and innovation by offering funding, resources, and collaboration opportunities with industry partners.
- Leadership Development Programmes: These programmes prepare trainers for advanced roles through leadership and management training and opportunities to take on leadership roles in projects and committees.
- Wellbeing and Work-Life Balance Initiatives: Support trainer wellbeing through employee assistance programmes, workshops on stress management, and flexible working arrangements.
Conclusion
Supporting the development of TVET trainers is fundamental to the success of vocational and technical education. By aligning support strategies with the Dreyfus and Dreyfus five-stage model, TVET organisations can enhance teaching quality, ensure training programmes remain relevant, meet the diverse needs of learners, and promote lifelong learning. Additionally, these efforts improve workforce readiness, encourage innovation, and enhance the well-being and satisfaction of trainers. Investing in the continuous professional development of trainers ensures that TVET organisations provide high-quality education that meets the evolving needs of learners and industries, ultimately contributing to economic and social development.



