Curriculum sequencing is a fundamental aspect of educational planning that ensures the structured and logical progression of knowledge and skills. It plays a pivotal role in the effectiveness of teaching and learning processes, significantly impacting learners’ ability to comprehend, retain, and apply the information they acquire. In the context of the OfSTED Education Inspection Framework, curriculum sequencing is critical for educational providers in England. This ebook explores the concept of curriculum sequencing and its significance and provides a step-by-step guide to designing an effective curriculum sequence.
Understanding Curriculum Sequencing
What is Curriculum Sequencing?
Curriculum sequencing refers to the methodical organisation of curriculum activities, which includes the arrangement of skills and knowledge presented throughout an educational program. It involves determining the order in which educational content is delivered, ensuring that each unit builds on the previous one, enabling a coherent and cumulative learning experience.
The Role of Curriculum Sequencing in Education
Effective curriculum sequencing is essential for several reasons:
- Facilitates Learning: It helps learners progressively develop their understanding and skills, making it easier to grasp complex concepts.
- Ensures Continuity: A well-sequenced curriculum ensures that there are no gaps in knowledge and that each learning activity connects logically with the next.
- Supports Assessment: Proper sequencing aligns learning activities with appropriate assessments, enabling accurate measurement of student progress and understanding.
- Enhances Retention: A sequenced curriculum aids in retaining and applying information by building on previous knowledge.
Curriculum Sequencing in the OfSTED Education Inspection Framework
The OfSTED Education Inspection Framework requires educational and training providers in England to plan and sequence their curriculums. The framework emphasises that:
- Curriculums should be designed to provide learners with the knowledge and skills needed for future learning and employment.
- Curriculum sequencing should ensure learners can demonstrate their understanding and application of acquired skills.
- Providers must continuously review and adapt their curriculum sequences to meet the evolving needs of learners.
The Importance of Curriculum Sequencing
Impact on Learners
A well-sequenced curriculum significantly benefits learners by:
- Enhancing Understanding: When new information is presented in a logical and coherent order, learners can better understand and internalise it.
- Building Confidence: As learners progress through a sequenced curriculum, they gain confidence in their ability to master new concepts and skills.
- Promoting Engagement: A thoughtfully sequenced curriculum maintains learner engagement by gradually increasing the complexity of tasks and challenges.
Implications for Educators
For educators, effective curriculum sequencing:
- Streamlines Planning: It provides a clear roadmap for delivering content, making lesson planning more efficient.
- Improves Instruction: Educators can tailor their teaching strategies to align with the curriculum sequence, ensuring that each lesson builds on previous knowledge.
- Facilitates Assessment: Sequencing aids in designing assessments that accurately reflect the progression of learner understanding and skills.
Consequences of Poor Sequencing
Inadequate curriculum sequencing can lead to several issues:
- Learning Gaps: Disjointed or poorly planned sequences can leave gaps in learners’ knowledge, hindering their overall understanding.
- Increased Frustration: Learners may struggle with mastering complex skills if foundational knowledge is not properly established.
- Reduced Motivation: A lack of logical progression can lead to disengagement and decreased motivation to learn.
Designing an Effective Curriculum Sequence
Step 1: Determine Programme Outcomes
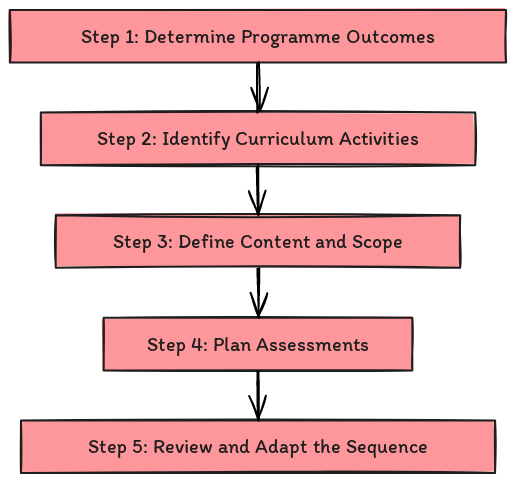
Begin the curriculum sequencing process by identifying the intended outcomes of your programme. This critical step aids in planning the curriculum intent and defining the overall purpose and direction of the programme.
Step 2: Identify Curriculum Activities
Next, establish the curriculum activities and consider the delivery order, ensuring that learners can acquire the requisite skills and knowledge cohesively and logically. The curriculum can be sequenced chronologically, thematically, or according to the level of difficulty.
Step 3: Define Content and Scope
Upon determining the sequence of activities, focus on the content and scope of each curriculum activity. Descriptions of each activity can help ascertain the expected outcomes. Additionally, it is essential to identify and develop the content for each activity, which can also support curriculum implementation planning.
Step 4: Plan Assessments
With the sequence of activities and content defined, proceed to plan the assessment for each activity. Assessments, which can be either formative or summative, should correspond to the learning objectives. While formative assessments provide feedback to teachers and learners, summative assessments evaluate whether learning objectives have been achieved. Assessment planning is a fundamental aspect of curriculum sequencing, ensuring that each activity aligns with the appropriate level of assessment.
Step 5: Review and Adapt the Sequence
Lastly, it is essential to review and, if necessary, adapt the curriculum sequence. Although the sequence is not set in stone, any changes should be cautiously planned and executed to avoid adverse effects on student learning.
Chapter 4: Curriculum Sequencing Tools
Stedfast’s Curriculum Planning Tools
Stedfast offers comprehensive curriculum planning tools designed to facilitate effective sequencing and monitoring of curriculum implementation and impact. These tools provide educators with the resources needed to design, manage, and review curriculum sequences effectively.
Features and Benefits
Stedfast’s tools offer several features and benefits:
- User-Friendly Interface: The tools are designed to be intuitive, making it easy for educators to plan and adjust curriculum sequences.
- Comprehensive Planning: Educators can plan the entire curriculum sequence, including content, activities, and assessments, in one place.
- Real-Time Monitoring: The tools enable real-time monitoring of curriculum implementation, allowing for timely adjustments to enhance learner outcomes.
- Impact Analysis: Stedfast’s tools provide insights into the impact of the curriculum sequence on learner performance, aiding in continuous improvement.
Implementation in Schools
Implementing Stedfast’s curriculum planning tools in schools involves several steps:
- Training Educators: Provide training sessions to ensure educators are familiar with the tools and their features.
- Customizing the Tools: Tailor the tools to align with the specific needs and goals of the school’s curriculum.
- Integrating with Existing Systems: Ensure seamless integration with existing educational systems and processes.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support and resources to assist educators in effectively using the tools.
Chapter 6: Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges in Curriculum Sequencing
- Resistance to Change: Educators may resist changes to the established curriculum sequence.
- Resource Limitations: Limited resources can hinder effective curriculum planning and sequencing.
- Assessment Alignment: Ensuring assessments align with the curriculum sequence can be challenging.
Solutions and Best Practices
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve all stakeholders, including educators, learners, and parents, in the curriculum planning process.
- Provide Training: Offer regular training sessions to equip educators with the skills needed for effective curriculum sequencing.
- Utilise Technology: Utilise technology, such as Stedfast’s planning tools, to streamline and enhance the sequencing process.
- Continuous Review: Establish a continuous review process to identify and address any issues in the curriculum sequence.
Conclusion
Curriculum sequencing is a critical component of effective educational planning. It ensures that learners can build on their knowledge and skills progressively, leading to improved comprehension, retention, and application of information. By following a systematic approach to curriculum sequencing and using tools like Stedfast, educators can design and implement curricula that meet the needs of their learners and prepare them for future learning and employment. Continuous review and adaptation are essential to maintain the effectiveness of the curriculum sequence and respond to the evolving needs of learners.
Effective curriculum sequencing is not just about arranging content in a logical order; it is about creating a cohesive learning journey that supports and challenges learners at every step. By understanding and applying the principles of curriculum sequencing, educators can significantly enhance the quality of education and contribute to the success and development of their learners.






