Curriculum designers play a pivotal role in instructional design, ensuring that educational programmes are well-structured, effective, and engaging for learners. They serve as the architects of learning experiences, meticulously developing curricula that impart knowledge and inspire and motivate students. Their work combines creativity, analytical thinking, and a deep understanding of educational theories and practices. By collaborating with subject matter experts and utilising cutting-edge educational technologies, curriculum designers create robust frameworks that cater to diverse learning needs and environments. This overview will explore the key responsibilities, essential skills, and best practices for curriculum designers and their significant impact on educational initiatives’ overall success. They are essential in bridging the gap between educational objectives and learner outcomes, ensuring educational programmes are relevant and transformative.
Key Responsibilities of Curriculum Designers
Curriculum designers are pivotal in the instructional design process, undertaking various tasks to ensure that educational programmes are effective and engaging. Their responsibilities begin with conducting a comprehensive needs analysis to identify knowledge gaps and define precise learning objectives, ensuring the curriculum meets the specific needs of learners. Developing a detailed curriculum framework follows, outlining the content, sequence, and delivery methods to provide a cohesive structure for the educational programme. Collaboration with subject matter experts (SMEs) is essential for ensuring the content’s accuracy and relevance, utilising SMEs’ expertise to create up-to-date and comprehensive material. Additionally, curriculum designers develop learning activities and assessments that align with learning objectives and further learner engagement, which are critical for measuring progress and effectiveness. Adapting the curriculum to various learning environments, whether online, face-to-face, or blended, ensures accessibility and flexibility. Continuous evaluation of the curriculum’s effectiveness through data analysis and feedback from learners and educators allows for ongoing improvements, maintaining the curriculum’s relevance and impact. These responsibilities collectively ensure that curriculum designers create robust and dynamic educational experiences that meet the evolving needs of learners.
Curriculum designers are responsible for various tasks in the instructional design process. These include:
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Conducting Needs Analysis | Identifying knowledge gaps and learning objectives ensures the curriculum addresses learners’ needs and aligns with educational goals. |
| Developing a Curriculum Framework | Creating a comprehensive structure that outlines an educational programme’s content, sequence, and delivery methods serves as the blueprint for the curriculum. |
| Collaborating with Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) | Ensuring content accuracy and relevance by working closely with SMEs, whose expertise helps develop current and comprehensive content. |
| Designing Learning Activities and Assessments | Creating activities and assessments that align with learning objectives and promote engagement is important for measuring learner progress and curriculum effectiveness. |
| Adapting to Various Learning Environments | Ensuring the curriculum is flexible enough to suit different learning environments and modalities, such as online, face-to-face, or blended learning. |
| Evaluating Curriculum Effectiveness | Continuously assessing the curriculum through data analysis and feedback from learners, educators, and stakeholders to maintain its relevance and effectiveness. |
Skills Required for Effective Curriculum Design
To succeed in the role of a curriculum designer, individuals must possess a diverse range of skills that collectively contribute to creating effective and engaging educational programmes. A strong foundation in instructional design theories and models, such as ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation), SAM (Successive Approximation Model), and Bloom’s Taxonomy, is essential for structuring and evaluating learning experiences. Effective communication and collaboration skills are important, enabling curriculum designers to work with various stakeholders, including educators, administrators, and subject matter experts (SMEs). This collaboration ensures the curriculum is accurate, relevant, and aligned with educational goals. Critical thinking and problem-solving abilities are necessary to navigate and address complex educational challenges, promoting innovative solutions that enhance learning outcomes. Creativity and innovation are equally important, as they drive the design of engaging and interactive learning experiences that capture learners’ interest and facilitate deeper understanding. Strong project management skills are key for overseeing the development and implementation of the curriculum, requiring meticulous organisational and time-management capabilities. Additionally, familiarity with educational technology, such as learning management systems (LMS) and other digital tools, is increasingly important in today’s instructional design landscape, ensuring that curriculum designers can effectively integrate technology to support and enhance the learning process.
To succeed in the role of a curriculum designer, individuals must possess a diverse range of skills:
| Skill or Knowledge Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Knowledge of Instructional Design Theories and Models | Familiarity with frameworks such as ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation), SAM (Successive Approximation Model), and Bloom’s Taxonomy is essential. |
| Effective Communication and Collaboration | Successful curriculum development requires working well with diverse stakeholders, including educators, administrators, and SMEs. |
| Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving | These skills help address complex educational challenges and develop innovative solutions. |
| Creativity and Innovation | Designing engaging and interactive learning experiences requires a creative approach. |
| Project Management | Overseeing the development and implementation of the curriculum involves strong organisational and management skills. |
| Familiarity with Educational Technology | Knowledge of learning management systems (LMS) and other educational tools is increasingly important in modern instructional design. |
Best Practices for Curriculum Design
To create effective and engaging educational programmes, curriculum designers should adhere to a set of best practices that ensure the curriculum is impactful and relevant. The process begins with defining clear and measurable learning objectives that align with the needs of learners and stakeholders. These objectives are the foundation for the entire curriculum, guiding all subsequent design decisions. Emphasising a learner-centred approach means focusing on the target audience’s needs, preferences, and goals to ensure the curriculum is engaging and relevant. Incorporating various instructional strategies and activities is another best practice, as it accommodates different learning styles and preferences, maximising learner engagement and effectiveness. Providing opportunities for real-world application is also essential; by enabling learners to apply their knowledge and skills in practical contexts, curriculum designers enhance retention and understanding. Finally, regularly evaluating and updating the curriculum ensures its effectiveness and relevance. Continuous assessment and revision, based on feedback and data analysis, ensure that the curriculum remains current and continues to meet the evolving needs of learners. By adhering to these best practices, curriculum designers can create robust educational programmes that generate meaningful and lasting learning experiences.
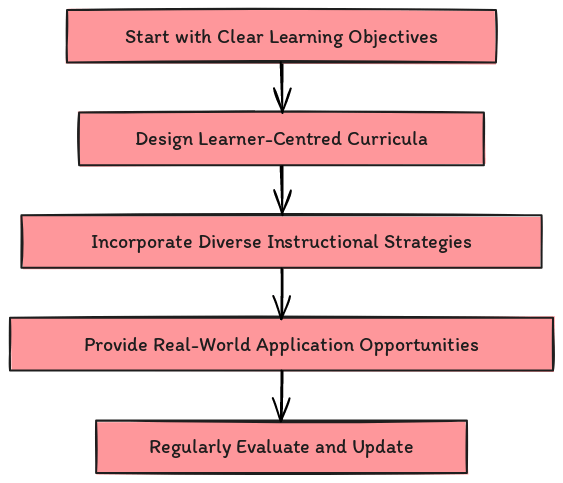
To create effective and engaging educational programmes, curriculum designers should adhere to the following best practices:
- Start with Clear Learning Objectives: Define measurable objectives that align with the needs of learners and stakeholders.
- Design Learner-Centred Curricula: Focus on the target audience’s needs, preferences, and goals to ensure relevance and engagement.
- Incorporate Diverse Instructional Strategies: Use various methods and activities to accommodate different learning styles and preferences.
- Provide Real-World Application Opportunities: Enable learners to apply their knowledge and skills in practical contexts, enhancing retention and understanding.
- Regularly Evaluate and Update: Continuously assess and revise the curriculum to maintain its effectiveness and relevance.
The Impact of Curriculum Designers on Educational Success
Curriculum designers shape the quality and effectiveness of educational programmes, significantly impacting educational success. Their efforts improve learner engagement and satisfaction, and well-designed curricula keep learners interested and motivated. Curriculum designers use effective instructional design principles to enhance knowledge retention and skill development, resulting in better learning outcomes and skill acquisition. Establishing clear objectives and well-structured activities ensures that learners achieve their educational goals, contributing to higher achievement of learning outcomes. Additionally, effective curricula prepare learners for assessments and real-world applications, leading to increased success rates in both academic and practical settings. Curriculum designers also ensure alignment with industry and societal needs by collaborating with stakeholders and staying current with industry trends. This alignment guarantees that educational programmes are relevant, up-to-date, and tailored to meet the evolving demands of the job market and society. Through these contributions, curriculum designers play an essential role in furthering educational excellence and preparing learners for future success.
Curriculum designers shape the quality and effectiveness of educational programmes. Their efforts contribute to:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Learner Engagement and Satisfaction | Well-designed curricula keep learners interested and motivated. |
| Enhanced Knowledge Retention and Skill Development | Effective instructional design improves learning outcomes and skill acquisition. |
| Higher Achievement of Learning Outcomes | Clear objectives and well-structured activities ensure learners achieve their educational goals. |
| Increased Success Rates in Assessments | Effective curricula prepare learners for assessments and real-world applications, leading to higher success rates. |
| Alignment with Industry and Societal Needs | Curriculum designers collaborate with stakeholders and stay current with industry trends to ensure that educational programmes meet the needs of society and the job market. |
Conclusion
The role of a curriculum designer is integral to the success of instructional design initiatives. Curriculum designers employ their expertise in needs analysis, content development, learning activity design, and evaluation to ensure that educational programmes are engaging, effective, and relevant for learners. As a result, they play a critical role in shaping the future success of students and the wider educational landscape.