Apprenticeships offer a unique learning experience by combining on-the-job training with theoretical knowledge. This dual approach not only equips apprentices with practical skills but also enhances their understanding of their trade or profession’s underlying principles and theories. However, the success of an apprenticeship programme heavily relies on a robust support system. In this article, we will investigate the significance of mentoring and guidance, the role of mentors, the benefits of a strong support system, and effective strategies for mentoring. Additionally, it will explore the role of the apprenticeship provider in facilitating the mentoring process.
The Importance of Mentoring and Guidance
Mentoring and guidance are critical components of the apprenticeship experience. They provide a structured pathway for apprentices to navigate their professional development. The guidance offered by experienced mentors helps apprentices assimilate into the workplace culture, understand job expectations, and develop a professional identity.
Benefits of a Strong Support System
A strong support system in apprenticeship programmes provides numerous benefits:
- Improved Skills Development: Mentors provide hands-on training and real-time feedback, accelerating skill acquisition and refinement.
- Increased Motivation: A supportive mentor can inspire apprentices, encouraging a sense of purpose and commitment to their career goals.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities: Apprentices develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills through guided learning, which is essential for professional success.
- Better Retention Rates: Apprentices who feel supported are more likely to complete their programmes and stay with their employers, reducing turnover rates.
Strategies for Effective Guidance
To ensure effective guidance, mentors should employ the following strategies:
- Establish Clear Expectations: Clearly define roles, responsibilities, and performance standards from the outset. This helps apprentices understand what is expected of them and what they can expect from their mentors.
- Promote Open Communication: Encourage a two-way dialogue where apprentices feel comfortable asking questions, expressing concerns, and sharing ideas. This openness builds trust and promotes a positive learning environment.
- Offer Constructive Feedback: Regular, actionable feedback helps apprentices improve their performance. Constructive criticism should be balanced with positive reinforcement to maintain motivation.
- Create Personalised Learning Plans: Tailor learning experiences to the individual needs of apprentices. Personalised plans should consider the apprentice’s strengths, weaknesses, and career aspirations.
- Encourage Self-reflection: Encourage apprentices to think about their experiences, identify learning points, and set future goals. Reflection helps deepen understanding and supports continuous improvement.
The Role of Apprenticeship Providers
Training providers are integral to the success of apprenticeship programmes. They serve as the bridge between the theoretical knowledge imparted in educational settings and the practical skills gained in the workplace. Training providers, including vocational schools, colleges, industry associations, and dedicated training organisations, play a multidimensional role in designing, implementing, and supporting apprenticeship programmes. Their involvement ensures that apprentices receive a well-rounded education that equips them with the skills to excel in their chosen careers.
Key Responsibilities of Training Providers
| Responsibility | Description |
|---|---|
| Curriculum Development | Training providers are responsible for developing and maintaining a curriculum that aligns with industry standards and employer needs. This involves continuous consultation with industry experts to ensure the training content is up-to-date, relevant, and comprehensive. |
| Accreditation and Certification | Training providers are critical in ensuring the apprenticeship programme meets regulatory and accreditation standards. They work to obtain and maintain necessary certifications, which validate the quality and rigour of the training provided. |
| Providing Educational Resources | Training providers offer a range of educational resources, including textbooks, online modules, workshops, and laboratory sessions. These resources complement on-the-job training and provide apprentices with a strong theoretical foundation. |
| Instructor Training and Support | To deliver high-quality training, providers must ensure their instructors are well-qualified and continuously improving their teaching methods. This includes offering professional development opportunities and resources to help instructors stay current with industry advancements. |
| Assessment and Evaluation | Training providers assess apprentices’ progress through regular evaluations and examinations. This helps ensure that apprentices meet learning objectives and allows for timely intervention if any issues arise. |
| Collaboration with Employers | Effective apprenticeship programmes require strong partnerships between training providers and employers. Providers work closely with companies to ensure the training aligns with real-world job requirements and facilitates smooth transitions between classroom learning and on-the-job training. |
| Mentor Selection and Training | Training providers assist employers in selecting suitable workplace mentors. They may also offer training programmes for mentors to equip them with the skills to guide and support apprentices effectively. |
| Monitoring and Support | Continuous monitoring of apprentices’ progress is pivotal. Training providers track apprentices’ development, offer support services, and address any academic or personal challenges that may arise during the apprenticeship. |
| Facilitating Networking Opportunities | Training providers often organise events, workshops, and seminars that allow apprentices to network with industry professionals, potential employers, and peers. These opportunities can be invaluable for career development and job placement. |
The Impact of Training Providers
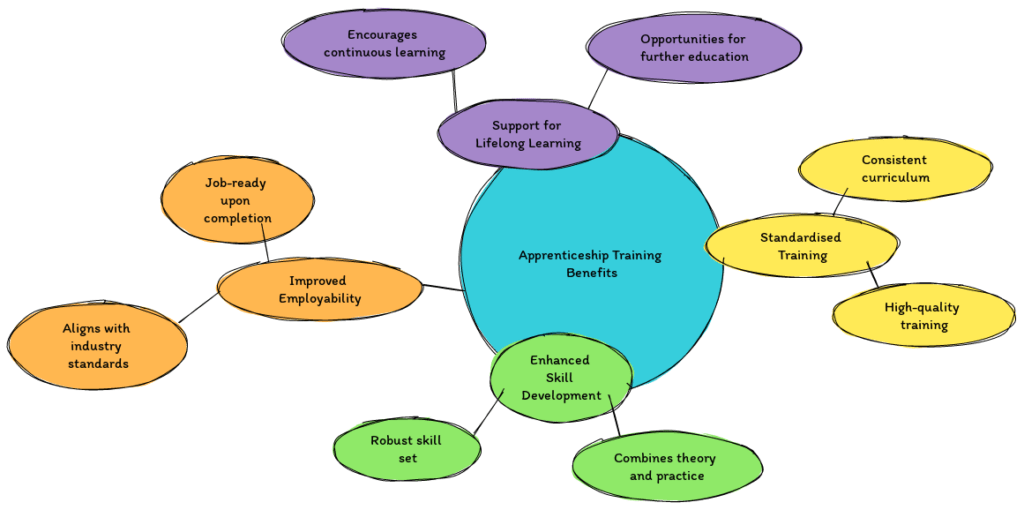
The involvement of training providers significantly enhances the quality and effectiveness of apprenticeship programmes. Their contributions lead to:
- Standardised Training: A consistent curriculum ensures that all apprentices receive the same high-quality training, regardless of their employer or location.
- Enhanced Skill Development: Comprehensive training programmes that combine theoretical and practical learning equip apprentices with a robust skill set that meets industry demands.
- Improved Employability: By aligning training with industry standards, providers help ensure that apprentices are job-ready upon completing their programmes, increasing their employability.
- Support for Lifelong Learning: Training providers often encourage a culture of continuous learning, offering opportunities for apprentices to pursue further education and professional development.
Challenges Faced by Training Providers
While training providers play a significant role, they also face several challenges:
- Keeping Up with Industry Changes: Rapid technological advancements and evolving industry standards require continuous updates to training programmes.
- Resource Constraints: Developing and maintaining high-quality training programmes can be resource-intensive, requiring significant investment in materials, facilities, and staff.
- Balancing Theory and Practice: Ensuring apprentices receive a balanced education with theoretical knowledge and practical skills can be challenging.
- Engaging Employers: Building and maintaining strong partnerships with employers is essential but can be difficult, especially in industries with high variability in job requirements.
Training providers are essential to the success of apprenticeship programmes, offering the structured education and support necessary to develop skilled and competent professionals. Training providers ensure that apprentices receive a comprehensive and relevant education by focusing on curriculum development, accreditation, resource provision, instructor support, and collaboration with employers. Overcoming their challenges and continuing to innovate and adapt will enable training providers to maintain their critical role in shaping the future workforce. Through their efforts, apprentices are better prepared to meet the demands of their industries, contributing to a skilled and dynamic labour market.
The Role of Workplace Mentors
Workplace mentors are essential pillars in the structure of apprenticeship programmes. They are not just experienced professionals but also guides who play a varied role in the development and success of apprentices. Their responsibilities extend beyond mere instruction; they encompass nurturing an environment of growth, offering emotional and professional support, and bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Key Responsibilities of Workplace Mentors
- Knowledge Transfer: Mentors are repositories of industry-specific knowledge and skills. They provide apprentices with detailed insights into their field, from technical know-how to industry best practices. This direct knowledge transfer helps apprentices acquire the expertise needed for their roles.
- Guidance and Support: Navigating a new workplace can be daunting for apprentices. Mentors guide them through this transition, offering advice on workplace norms, professional behaviour, and effective communication. They help apprentices understand the company culture and integrate smoothly into the team.
- Providing Feedback: Constructive feedback is fundamental for learning and development. Mentors regularly assess apprentices’ performance, identify areas for improvement, and provide actionable suggestions. This feedback helps apprentices refine their skills and encourages continuous improvement.
- Role Modeling: Mentors exemplify the professional standards and behaviours expected in the workplace. Apprentices learn about work ethic, problem-solving strategies, and professional conduct by observing and interacting with their mentors. This modelling helps apprentices develop their own professional identity.
- Emotional Support: Starting a new career can be stressful. Mentors offer emotional support, helping apprentices manage stress, build confidence, and develop resilience. They provide a safe space for apprentices to express concerns and discuss challenges, creating a supportive learning environment.
- Networking Opportunities: Mentors often have extensive professional networks. They can introduce apprentices to key industry contacts, helping them build their networks. This networking can open doors to future career opportunities and professional growth.
Impact of Effective Mentoring
The presence of a dedicated mentor significantly enhances the apprenticeship experience. Effective mentoring leads to:
- Accelerated Learning: Direct, hands-on guidance helps apprentices acquire and apply new skills quickly.
- Increased Confidence: Regular support and positive reinforcement boost apprentices’ confidence in their abilities.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: Mentors teach apprentices to approach problems methodically and creatively, improving their problem-solving capabilities.
- Higher Retention Rates: Apprentices who feel supported and valued are likelier to stay with their employer, reducing turnover.
- Career Advancement: Mentors help apprentices set and achieve career goals, positioning them for long-term success.
Challenges and Considerations for Mentors
While mentoring is rewarding, it also comes with challenges:
- Time Commitment: Effective mentoring requires a significant investment of time and energy. Mentors must balance their responsibilities with their mentoring duties.
- Skill Development: Not all experienced professionals naturally possess mentoring skills. Training and resources can help mentors develop the necessary skills to guide and support apprentices effectively.
- Relationship Building: Establishing a trusting and productive mentor-apprentice relationship takes time and effort. Open communication and mutual respect are key to building this relationship.
Workplace mentors are indispensable to the success of apprenticeship programmes. They provide the knowledge, guidance, and support apprentices need to prosper. By investing in effective mentoring, companies enhance their apprentices’ skills and confidence and generate a culture of continuous learning and professional development. This investment ultimately benefits the apprentices and the organisation, leading to a more skilled, motivated, and engaged workforce.
Conclusion
Supporting apprentices through mentoring and guidance is essential for their success. Apprenticeship providers can help apprentices advance in their chosen careers by providing experienced mentors, a strong support system, and effective guidance strategies. By breeding a mentoring culture and providing necessary resources, apprentices and mentors can enjoy a positive and rewarding experience. This, in turn, ensures that apprentices are well-prepared for their professional journeys, contributing to a skilled and motivated workforce.



